| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 |
- stream
- datastructure
- s
- Stack
- Serialization
- 혼자 공부하는 C언어
- 윤성우의 열혈 자료구조
- 이것이 자바다
- Graph
- Selection Sorting
- R
- 알기쉬운 알고리즘
- 윤성우 열혈자료구조
- C programming
- 메모리구조
- buffer
- C 언어 코딩 도장
- coding test
- 이스케이프 문자
- JSON
- insertion sort
- Algorithm
- list 컬렉션
- Today
- Total
Engineering Note
[SW Engineering] 페이지네이션 성능 측정 최적화(Offset vs Cursor Pagination 성능 비교 (평균 17배 개선)) 본문
[SW Engineering] 페이지네이션 성능 측정 최적화(Offset vs Cursor Pagination 성능 비교 (평균 17배 개선))
Software Engineer Kim 2025. 9. 8. 20:20문제 정의
상품 조회 기능을 개발할 때, JPA의 쿼리메서드를 사용하여 개발하면 성능의 문제는 없을지 문제의식을 가졌고, 직접 실험해보면서 문제를 해결하였습니다.
상품 조회 Pagination 기능을 개발할 때, findall JPA 쿼리 메서드를 사용한 Pagination과 Cursor 기반 Pagination에 대해 실제 실행되는 Query를 비교하고 성능 측정하여, 어떤 문제가 발생하는지 확인하고 적합한 Pagination 기능을 위한 기술을 선택하게 된 과정.
개발환경
- Java(17), Spring Boot(3), MySQL(9.0), JPA/Hibernate
상황설명
- JPA의 Pageable 타입을 매개변수로 받는 findall를 이용한 페이지 조회에서 무한스크롤 지원 API를 위해 조회 성능 테스트
- Product 테이블에 상품 데이터 300,000건이 저장, Page 별 Size는 100 건으로 마지막 페이지를 조회하는 상황
요청 API
# Offset 기반
GET <http://localhost:8080/api/products-offset?page=2999&size=100>
# Cursor 기반
GET <http://localhost:8080/api/products-cursor?startId=299900&pageSize=100>
Query 비교, 성능 측정
- findall 메서드 상품조회 pagination 코드 및 Query (offset 기반)
JPA findall 메서드 상품 조회 서비스 코드
public ProductsResponse getProductsByOffset(Pageable pageable) {
List<Product> productPage = productRepository.findAll(pageable).getContent();
return ProductsResponse.of(productPage);
}
실제 질의된 Database Query
select p1_0.id,p1_0.name,p1_0.price,p1_0.stock
from product p1_0
limit 299900,100;
findall 메서드를 통한 상품을 조회했을 때 limit를 이용한 offset 기반 query가 수행되었습니다.
- 직접 작성한 where 조건절을 통한 상품 조회 pagination(cursor 기반)
productRepository 코드
@Query(value = "select * from product p where p.id >= :id limit :pageSize", nativeQuery = true)
List<Product> findAllByCursor(@Param("id") Long id, @Param("pageSize") int pageSize);
findAllByCursor 메서드를 이용한 상품 조회 서비스 코드
public ProductsResponse getProductsByCursor(Long startId, int pageSize) {
List<Product> productPage = productRepository.findAllByCursor(startId, pageSize);
return ProductsResponse.of(productPage);
}
실제 질의된 Database Query
select *
from product p
where p.id >= 299901
limit 100;
두 방식의 상품 조회 기능을 구현하고 테스트 코드를 이용해 성능을 측정했다. 측정 방법은 서비스 코드 호출전과 후의 시스템 시간차이를 통해 latency time을 측정하였고, 정확한 평가를 위해 100번 요청후 평균값을 비교하였습니다.
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest;
import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles;
@ActiveProfiles("test")
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class ProductServiceTest {
private final static int ITERATION_COUNT = 100;
private final static int PAGE_SIZE = 100;
private final static int PAGE_NUMBER = 2999;
private final static int START_ID = 299901;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
@DisplayName("상품 목록 offset 기반 조회 성능 테스트")
@Test
void getProductsByOffset() {
// given
PageRequest pageRequest = PageRequest.of(PAGE_NUMBER, PAGE_SIZE);
// when
long totalTime = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < ITERATION_COUNT; i++) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("시작시간"+startTime);
productService.getProductsByOffset(pageRequest);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
totalTime += endTime - startTime;
}
// then
log.info("---- Offset 기반 성능 평가 ----");
log.info("Total time: " + totalTime + " ms");
log.info("Average time: " + totalTime / ITERATION_COUNT + " ms");
}
@DisplayName("상품 목록 cursor 기반 조회 성능 테스트")
@Test
void getProductsByCursor() {
// when
long totalTime = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < ITERATION_COUNT; i++) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
productService.getProductsByCursor((long) START_ID, PAGE_SIZE);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
totalTime += endTime - startTime;
}
// then
log.info("---- Cursor 기반 성능 평가 ----");
log.info("Total time: " + totalTime + " ms");
log.info("Average time: " + totalTime / ITERATION_COUNT + " ms");
}
}
성능 측정 결과
- findAll JPA Query Method vs Where, Cursor 기반 Native Query
- findall 메서드를 통한 상품 조회(offset 기반)

- 2. where 조건절 기반 native query 상품 조회(cursor 기반)
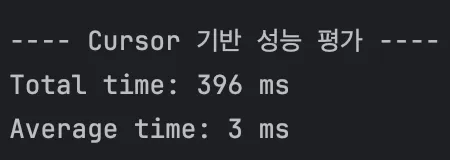
성능 측정 결과
cursor 기반이 paginationdl offset 기반대비 17배 빠른 성능을 보였다. 이러한 결과를 바탕으로, cursor 기반으로 pagination을 통한 무한 스크롤 지원 상품 조회 API를 구현하였습니다.
구현 과정중에서 하나의 API를 통해 최초 상품 페이지 진입하였을 경우와 다음 상품 조회 기능을 같은 API를 사용할 수 있도록 확장성을 고려하여 API를 설계하였습니다.
JPA의 findall(Pageable page)메서드는 데이터수가 적은 경우에는 문제가 없었지만, 상품 데이터 수에 대해 조회 페이지가 늘어남에 따라 무한스크롤에서 성능이 지연되는 문제가 있어서 cursor기반의 query를 직접 작성하여 pagination을 구현하였습니다.
실제 구현 결과
cursor 기반 상품 조회 API controller
@GetMapping("/products")
public ApiResponse<ProductsResponse> getProducts(
@RequestParam(required = false) Long cursor,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "20") int pageSize) {
ProductsResponse response = productService.getProducts(cursor, pageSize);
return ApiResponse.success(response);
}
상품 조회 서비스 코드
public ProductsResponse getProducts(Long cursor, int pageSize) {
List<Product> products;
if (cursor == null) {
// 첫 페이지
products = productRepository.findFirstPage(pageSize);
} else {
products = productRepository.findAllByCursor(cursor, pageSize);
}
Long nextCursor = products.isEmpty() ? null :
products.get(products.size() - 1).getId();
boolean hasNext = products.size() == pageSize;
return ProductsResponse.of(products, nextCursor, hasNext, pageSize);
}
'SW Engineering' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [SW Engineering] Spring Boot 배포 최적화 (0) | 2025.09.18 |
|---|---|
| [SW Engineering] 동시성 문제 테스트 환경 구축기 (0) | 2025.09.09 |
| [SW Engineering] 비동기 통신 직접 만들면서 익히기 (0) | 2025.07.21 |
| 동기(Synchronous) vs 비동기(Asynchronous) (2) | 2025.06.17 |
| 다양한 JSON 구조와 Java Class 매핑 하기 (0) | 2025.03.30 |

